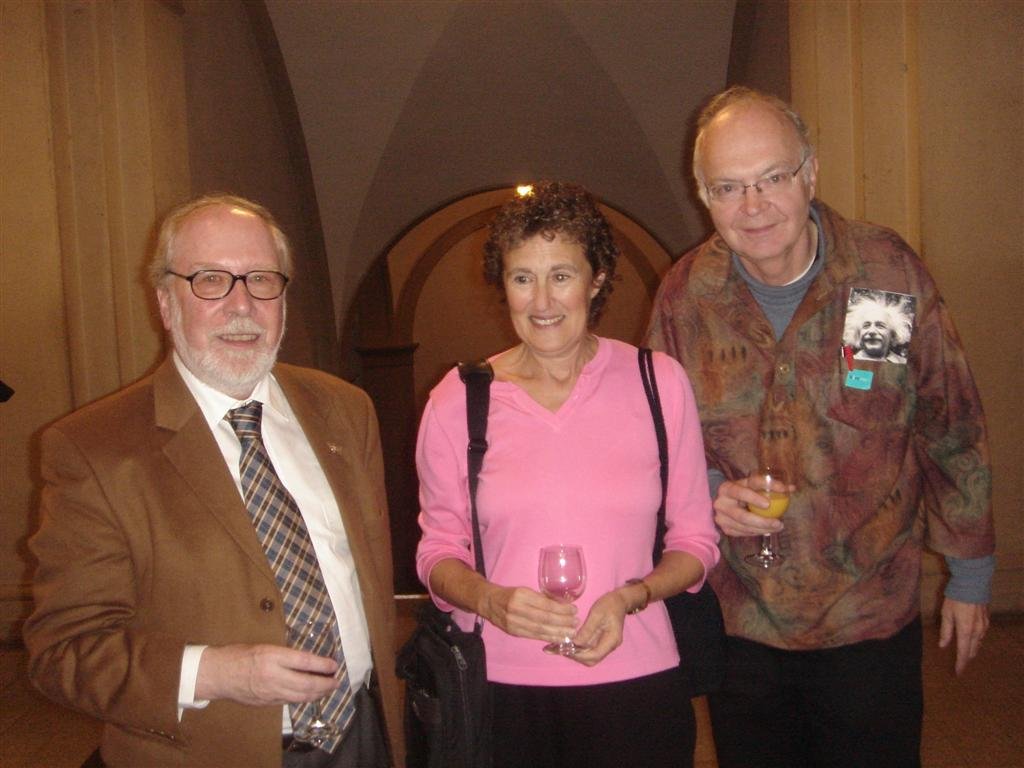[This is a verbatim copy of a post in the Communications of the ACM blog, 9 January 2024.]
I am still in shock from the unexpected death of Niklaus Wirth eight days ago. If you allow a personal note (not the last one in this article): January 11, two days from now, was inscribed in my mind as the date of the next time he was coming to my home for dinner. Now it is the date set for his funeral.

Niklaus Wirth at the ACM Turing centenary celebration
San Francisco, 16 June 2012
(all photographs in this article are by B. Meyer)
A more composed person would wait before jotting down thoughts about Wirth’s contributions but I feel I should do it right now, even at the risk of being biased by fresh emotions.
Maybe I should first say why I have found myself, involuntarily, writing obituaries of computer scientists: Kristen Nygaard and Ole-Johan Dahl, Andrey Ershov, Jean Ichbiah, Watts Humphrey, John McCarthy, and most recently Barry Boehm (the last three in this very blog). You can find the list with comments and links to the eulogy texts on the corresponding section of my publication page. The reason is simple: I have had the privilege of frequenting giants of the discipline, tempered by the sadness of seeing some of them go away. (Fortunately many others are still around and kicking!) Such a circumstance is almost unbelievable: imagine someone who, as a student and young professional, discovered the works of Galileo, Descartes, Newton, Ampère, Faraday, Einstein, Planck and so on, devouring their writings and admiring their insights — and later on in his career got to meet all his heroes and conduct long conversations with them, for example in week-long workshops, or driving from a village deep in Bavaria (Marktoberdorf) to Munich airport. Not possible for a physicist, of course, but exactly the computer science equivalent of what happened to me. It was possible for someone of my generation to get to know some of the giants in the field, the founding fathers and mothers. In my case they included some of the heroes of programming languages and programming methodology (Wirth, Hoare, Dijkstra, Liskov, Parnas, McCarthy, Dahl, Nygaard, Knuth, Floyd, Gries, …) whom I idolized as a student without every dreaming that I would one day meet them. It is natural then to should share some of my appreciation for them.
My obituaries are neither formal, nor complete, nor objective; they are colored by my own experience and views. Perhaps you object to an author inserting himself into an obituary; if so, I sympathize, but then you should probably skip this article and its companions and go instead to Wikipedia and official biographies. (In the same vein, spurred at some point by Paul Halmos’s photographic record of mathematicians, I started my own picture gallery. I haven’t updated it recently, and the formatting shows the limits of my JavaScript skills, but it does provide some fresh, spontaneous and authentic snapshots of famous people and a few less famous but no less interesting ones. You can find it here. The pictures of Wirth accompanying this article are taken from it.)
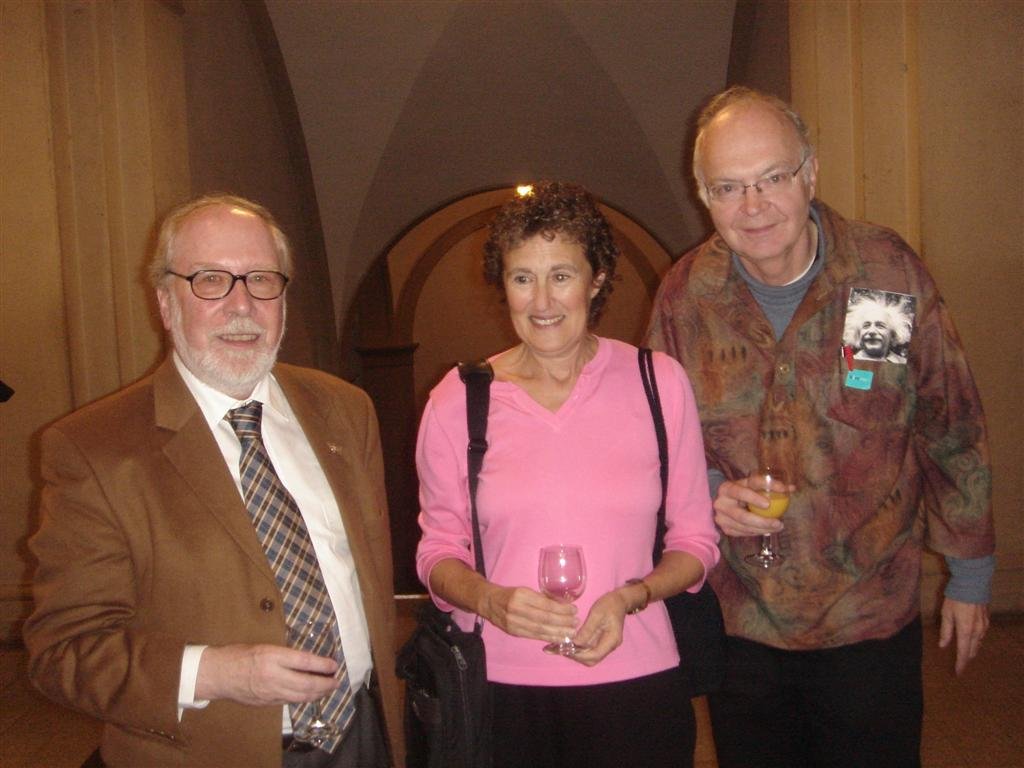
Niklaus Wirth, Barbara Liskov, Donald Knuth
(ETH Zurich, 2005, on the occasion of conferring honorary doctorates to Liskov and Knuth)
A peculiarity of my knowledge of Wirth is that unlike his actual collaborators, who are better qualified to talk about his years of full activity, I never met him during that time. I was keenly aware of his work, avidly getting hold of anything he published, but from a distance. I only got to know him personally after his retirement from ETH Zurich (not surprisingly, since I joined ETH because of that retirement). In the more than twenty years that followed I learned immeasurably from conversations with him. He helped me in many ways to settle into the world of ETH, without ever imposing or interfering.
I also had the privilege of organizing in 2014, together with his longtime colleague Walter Gander, a symposium in honor of his 80th birthday, which featured a roster of prestigious speakers including some of the most famous of his former students (Martin Oderski, Clemens Szyperski, Michael Franz…) as well as Vint Cerf. Like all participants in this memorable event (see here for the program, slides, videos, pictures…) I learned more about his intellectual rigor and dedication, his passion for doing things right, and his fascinating personality.
Some of his distinctive qualities are embodied in a book published on the occasion of an earlier event, School of Niklaus Wirth: The Art of Simplicity (put together by his close collaborator Jürg Gutknecht together with Laszlo Boszormenyi and Gustav Pomberger; see the Amazon page). The book, with its stunning white cover, is itself a model of beautiful design achieved through simplicity. It contains numerous reports and testimonials from his former students and colleagues about the various epochs of Wirth’s work.

Niklaus Wirth (right)
with F.L. Bauer, one of the founders of German computer science
Zurich,22 June 2005
Various epochs and many different topics. Like a Renaissance man, or one of those 18-th century “philosophers” who knew no discipline boundaries, Wirth straddled many subjects. It was in particular still possible (and perhaps necessary) in his generation to pay attention to both hardware and software. Wirth is most remembered for his software work but he was also a hardware builder. The influence of his PhD supervisor, computer design pioneer and UC Berkeley professor Harry Huskey, certainly played a role.
Stirred by the discovery of a new world through two sabbaticals at Xerox PARC (Palo Alto Research Center, the mother lode of invention for many of today’s computer techniques) but unable to bring the innovative Xerox machines to Europe, Wirth developed his own modern workstations, Ceres and Lilith. (Apart from the Xerox stays, Wirth spent significant time in the US and Canada: University of Laval for his master degree, UC Berkeley for his PhD, then Stanford, but only as an assistant professor, which turned out to be Switzerland’s and ETH’s gain, as he returned in 1968,)
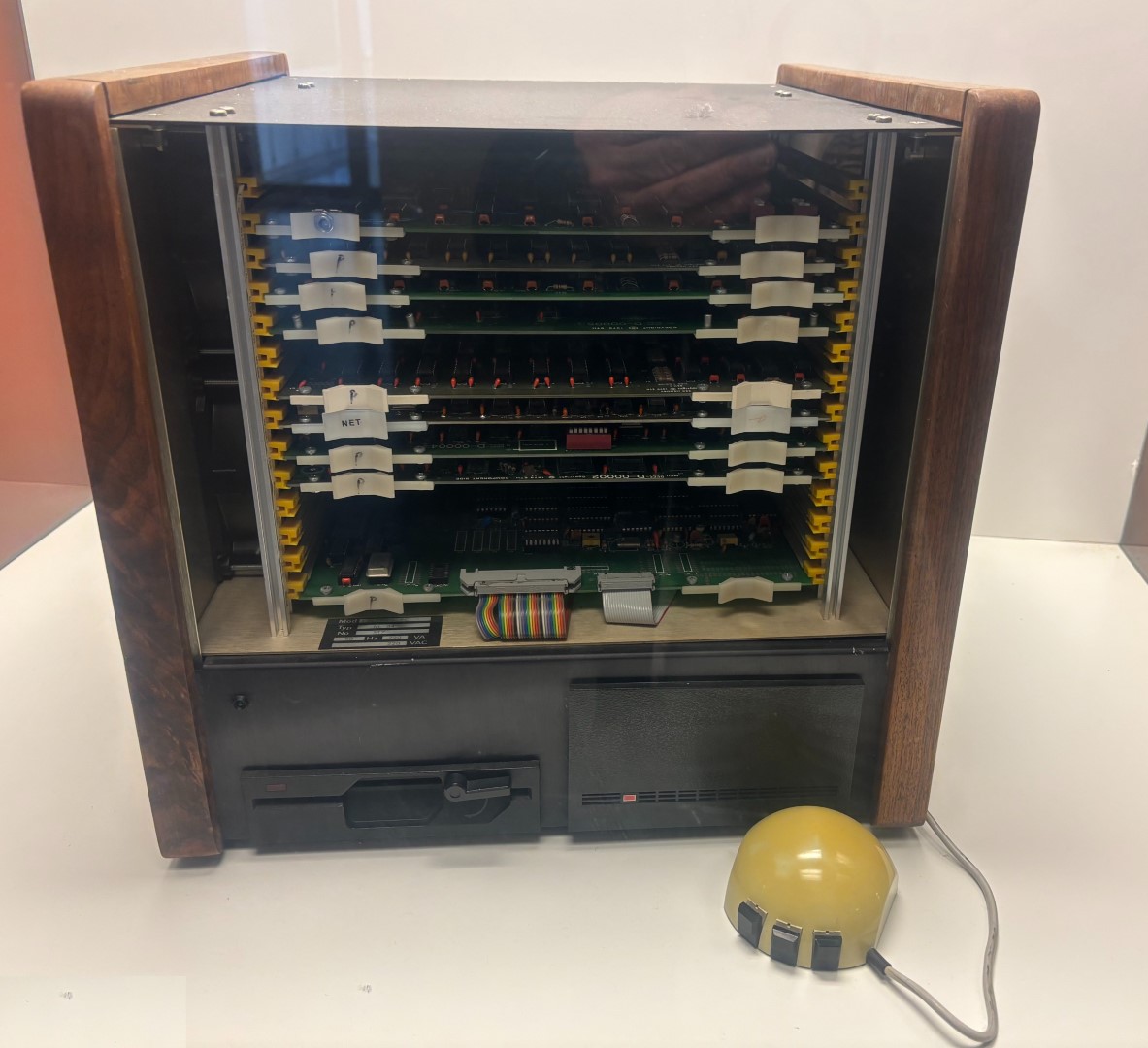

Lilith workstation and its mouse
(Public display in the CAB computer science building at ETH Zurich)
One of the Xerox contributions was the generalized use of the mouse (the invention of Doug Englebart at the nearby SRI, then the Stanford Research Institute). Wirth immediately seized on the idea and helped found the Logitech company, which soon became, and remains today, a world leader in mouse technology.
Wirth returned to hardware-software codesign late in his career, in his last years at ETH and beyond, to work on self-driving model helicopters (one might say to big drones) with a Strong-ARM-based hardware core. He was fascinated by the goal of maintaining stability, a challenge involving physics, mechanical engineering, electronic engineering in addition to software engineering.
These developments showed that Wirth was as talented as an electronics engineer and designer as he was in software. He retained his interest in hardware throughout his career; one of his maxims was indeed that the field remains driven by hardware advances, which make software progress possible. For all my pride as a software guy, I must admit that he was largely right: object-oriented programming, for example, became realistic once we had faster machines and more memory.
Software is of course what brought him the most fame. I struggle not to forget any key element of his list of major contributions. (I will come back to this article when emotions abate, and will add a proper bibliography of the corresponding Wirth publications.) He showed that it was possible to bring order to the world of machine-level programming through his introduction of the PL/360 structured assembly language for the IBM 360 architecture. He explained top-down design (“stepwise refinement“), as no one had done before, in a beautiful article that forever made the eight-queens problem famous. While David Gries had in his milestone book Compiler Construction for Digital Computers established compiler design as a systematic discipline, Wirth showed that compilers could be built simply and elegantly through recursive descent. That approach had a strong influence on language design, as will be discussed below in relation to Pascal.
The emphasis simplicity and elegance carried over to his book on compiler construction. Another book with the stunning title Algorithms + Data Structures = Programs presented a clear and readable compendium of programming and algorithmic wisdom, collecting the essentials of what was known at the time.
And then, of course, the programming languages. Wirth’s name will forever remained tied to Pascal, a worldwide success thanks in particular to its early implementations (UCSD Pascal, as well as Borland Pascal by his former student Philippe Kahn) on microcomputers, a market that was exploding at just that time. Pascal’s dazzling spread was also helped by another of Wirth’s trademark concise and clear texts, the Pascal User Manual and Report, written with Kathleen Jensen. Another key component of Pascal’s success was the implementation technique, using a specially designed intermediate language, P-Code, the ancestor of today’s virtual machines. Back then the diversity of hardware architectures was a major obstacle to the spread of any programming language; Wirth’s ETH compiler produced P-Code, enabling anyone to port Pascal to a new computer type by writing a translator from P-Code to the appropriate machine code, a relatively simple task.
Here I have a confession to make: other than the clear and simple keyword-based syntax, I never liked Pascal much. I even have a snide comment in my PhD thesis about Pascal being as small, tidy and exciting as a Swiss chalet. In some respects, cheekiness aside, I was wrong, in the sense that the limitations and exclusions of the language design were precisely what made compact implementations possible and widely successful. But the deeper reason for my lack of enthusiasm was that I had fallen in love with earlier designs from Wirth himself, who for several years, pre-Pascal, had been regularly churning out new language proposals, some academic, some (like PL/360) practical. One of the academic designs I liked was Euler, but I was particularly keen about Algol W, an extension and simplification of Algol 60 (designed by Wirth with the collaboration of Tony Hoare, and implemented in PL/360). I got to know it as a student at Stanford, which used it to teach programming. Algol W was a model of clarity and elegance. It is through Algol W that I started to understand what programming really is about; it had the right combination of freedom and limits. To me, Pascal, with all its strictures, was a step backward. As an Algol W devotee, I felt let down.
Algol W played, or more precisely almost played, a historical role. Once the world realized that Algol 60, a breakthrough in language design, was too ethereal to achieve practical success, experts started to work on a replacement. Wirth proposed Algol W, which the relevant committee at IFIP (International Federation for Information Processing) rejected in favor of a competing proposal by a group headed by the Dutch computer scientist (and somewhat unrequited Ph.D. supervisor of Edsger Dijkstra) Aad van Wijngaarden.
Wirth recognized Algol 68 for what it was, a catastrophe. (An example of how misguided the design was: Algol 68 promoted the concept of orthogonality, roughly stating that any two language mechanisms could be combined. Very elegant in principle, and perhaps appealing to some mathematicians, but suicidal: to make everything work with everything, you have to complicate the compiler to unbelievable extremes, whereas many of these combinations are of no use whatsoever to any programmer!) Wirth was vocal in his criticism and the community split for good. Algol W was a casualty of the conflict, as Wirth seems to have decided in reaction to the enormity of Algol 68 that simplicity and small size were the cardinal virtues of a language design, leading to Pascal, and then to its modular successors Modula and Oberon.
Continuing with my own perspective, I admired these designs, but when I saw Simula 67 and object-oriented programming I felt that I had come across a whole new level of expressive power, with the notion of class unifying types and modules, and stopped caring much for purely modular languages, including Ada as it was then. A particularly ill-considered feature of all these languages always irked me: the requirement that every module should be declared in two parts, interface and implementation. An example, in my view, of a good intention poorly realized and leading to nasty consequences. One of these consequences is that the information in the interface part inevitably gets repeated in the implementation part. Repetition, as David Parnas has taught us, is (particularly in the form of copy-paste) the programmer’s scary enemy. Any change needs to be checked and repeated in both the original and the duplicate. Any bug needs to be fixed in both. The better solution, instead of the interface-implementation separation, is to write everything in one place (the class of object-oriented programming) and then rely on tools to extract, from the text, the interface view but also many other interesting views abstracted from the text.
In addition, modular languages offer one implementation for each interface. How limiting! With object-oriented programming, you use inheritance to provide a general version of an abstraction and then as many variants as you like, adding them as you see fit (Open-Closed Principle) and not repeating the common information. These ideas took me towards a direction of language design completely different from Wirth’s.
One of his principles in language design was that it should be easy to write a compiler — an approach that paid off magnificently for Pascal. I mentioned above the beauty of recursive-descent parsing (an approach which means roughly that you parse a text by seeing how it starts, deducing the structure that you expect to follow, then applying the same technique recursively to the successive components of the expected structure). Recursive descent will only work well if the language is LL (1) or very close to it. (LL (1) means, again roughly, that the first element of a textual component unambiguously determines the syntactic type of that component. For example the instruction part of a language is LL (1) if an instruction is a conditional whenever it starts with the keyword if, a loop whenever it starts with the keyword while, and an assignment variable := expression whenever it starts with a variable name. Only with a near-LL (1) structure is recursive descent recursive-decent.) Pascal was designed that way.
A less felicitous application of this principle was Wirth’s insistence on one-pass compilation, which resulted in Pascal requiring any use of indirect recursion to include an early announcement of the element — procedure or data type — being used recursively. That is the kind of thing I disliked in Pascal: transferring (in my opinion) some of the responsibilities of the compiler designer onto the programmer. Some of those constraints remained long after advances in hardware and software made the insistence on one-pass compilation seem obsolete.
What most characterized Wirth’s approach to design — of languages, of machines, of software, of articles, of books, of curricula — was his love of simplicity and dislike of gratuitous featurism. He most famously expressed this view in his Plea for Lean Software article. Even if hardware progress drives software progress, he could not accept what he viewed as the lazy approach of using hardware power as an excuse for sloppy design. I suspect that was the reasoning behind the one-compilation-pass stance: sure, our computers now enable us to use several passes, but if we can do the compilation in one pass we should since it is simpler and leaner.
As in the case of Pascal, this relentless focus could be limiting at times; it also led him to distrust artificial intelligence, partly because of the grandiose promises its proponents were making at the time. For many years indeed, AI never made it into ETH computer science. I am talking here of the classical, logic-based form of AI; I had not yet had the opportunity to ask Niklaus what he thought of the modern, statistics-based form. Perhaps the engineer in him would have mollified his attitude, attracted by the practicality and well-defined scope of today’s AI methods. I will never know.
As to languages, I was looking forward to more discussions; while I wholeheartedly support his quest for simplicity, size to me is less important than simplicity of the structure and reliance on a small number of fundamental concepts (such as data abstraction for object-oriented programming), taken to their full power, permeating every facet of the language, and bringing consistency to a powerful construction.
Disagreements on specifics of language design are normal. Design — of anything — is largely characterized by decisions of where to be dogmatic and where to be permissive. You cannot be dogmatic all over, or will end with a stranglehold. You cannot be permissive all around, or will end with a mess. I am not dogmatic about things like the number of compiler passes: why care about having one, two, five or ten passes if they are fast anyway? I care about other things, such as the small number of basic concepts. There should be, for example, only one conceptual kind of loop, accommodating variants. I also don’t mind adding various forms of syntax for the same thing (such as, in object-oriented programming, x.a := v as an abbreviation for the conceptually sound x.set_a (v)). Wirth probably would have balked at such diversity.
In the end Pascal largely lost to its design opposite, C, the epitome of permissiveness, where you can (for example) add anything to almost anything. Recent languages went even further, discarding notions such as static types as dispensable and obsolete burdens. (In truth C is more a competitor to P-Code, since provides a good target for compilers: its abstraction level is close to that of the computer and operating system, humans can still with some effort decipher C code, and a C implementation is available by default on most platforms. A kind of universal assembly language. Somehow, somewhere, the strange idea creeped into people’s minds that it could also be used as a notation for human programmers.)
In any case I do not think Niklaus followed closely the evolution of the programming language field in recent years, away from principles of simplicity and consistency; sometimes, it seems, away from any principles at all. The game today is mostly “see this cute little feature in my language, I bet you cannot do as well in yours!” “Oh yes I can, see how cool my next construct is!“, with little attention being paid to the programming language as a coherent engineering construction, and even less to its ability to produce correct, robust, reusable and extendible software.
I know Wirth was horrified by the repulsive syntax choices of today’s dominant languages; he could never accept that a = b should mean something different from b = a, or that a = a + 1 should even be considered meaningful. The folly of straying away from conventions of mathematics carefully refined over several centuries (for example by distorting “=” to mean assignment and resorting to a special symbol for equality, rather than the obviously better reverse) depressed him. I remain convinced that the community will eventually come back to its senses and start treating language design seriously again.
One of the interesting features of meeting Niklaus Wirth the man, after decades of studying from the works of Professor Wirth the scientist, was to discover an unexpected personality. Niklaus was an affable and friendly companion, and most strikingly an extremely down-to-earth person. On the occasion of the 2014 symposium we were privileged to meet some of his children, all successful in various walks of life: well-known musician in the Zurich scene, specialty shop owner… I do not quite know how to characterize in words his way of speaking (excellent) English, but it is definitely impossible to forget its special character, with its slight but unmistakable Swiss-German accent (also perceptible in German). To get an idea, just watch one of the many lecture videos available on the Web. See for example the videos from the 2014 symposium mentioned above, or this full-length interview recorded in 2018 as part of an ACM series on Turing Award winners.
On the “down-to-earth” part: computer scientists, especially of the first few generations, tend to split into the mathematician types and the engineer types. He was definitely the engineer kind, as illustrated by his hardware work. One of his maxims for a successful career was that there are a few things that you don’t want to do because they are boring or feel useless, but if you don’t take care of them right away they will come back and take even more of your time, so you should devote 10% of that time to discharge them promptly. (I wish I could limit that part to 10%.)
He had a witty, subtle — sometimes caustic — humor. Here is a Niklaus Wirth story. On the seventh day of creation God looked at the result. (Side note: Wirth was an atheist, which adds spice to the choice of setting for the story.) He (God) was pretty happy about it. He started looking at the list of professions and felt good: all — policeman, minister, nurse, street sweeper, interior designer, opera singer, personal trainer, supermarket cashier, tax collector… — had some advantages and some disadvantages. But then He got to the University Professor row. The Advantages entry was impressive: long holidays, decent salary, you basically get to do what you want, and so on; but the Disadvantages entry was empty! Such a scandalous discrepancy could not be tolerated. For a moment, a cloud obscured His face. He thought and thought and finally His smile came back. At that point, He had created colleagues.
When the computing world finally realizes that design needs simplicity, it will do well to go back to Niklaus Wirth’s articles, books and languages. I can think of only a handful of people who have shaped the global hardware and software industry in a comparable way. Niklaus Wirth is, sadly, sadly gone — and I still have trouble accepting that he will not show up for dinner, on Thursday or ever again — but his legacy is everywhere.